Jiangsu Province Laboratory Animal License Annual Inspection Report
Release date:
2024-02-05
Jiangsu Province Laboratory Animal License
Annual Inspection Report
Unit Name (Official Seal): Shengshi Taikang Biopharmaceutical Technology (Suzhou) Co., Ltd.
Location: Suzhou Free Trade Zone
License Status: Use
Responsible official in charge of the unit: Lu Qin Contact number: 051262956960
Submitter: Ding Juping Contact number: 15162421238
Submission Date: February 5, 2024
Office of the Jiangsu Provincial Committee for Laboratory Animal Management
| Unit Name ( Legal entity ) |
Shengshi Taikang Biopharmaceutical Technology (Suzhou) Co., Ltd. |
Legal Representative |
Ding Juping |
|
| Unit Address |
Suzhou Industrial Park, Bio-Nano Park Phase I, Xinghu Street C11-101, 102 |
Unit Website |
https://www.cgenetech.com.cn/ |
|
| Laboratory animals The competent authority of the unit |
Department of Biology |
Department Head and Landline Phone |
Lu Qin 051262956960 |
|
| Laboratory animals Regarding qualifications |
China |
|||
| Is it located within the park premises? (Such as the science park, high-tech zone, incubator, etc.) |
No |
Does the organization qualify as a high-tech enterprise? |
No |
|
| Management Compliance Status |
Is there any violation of research integrity? |
No |
||
| Is there any violation of safe production practices? |
No |
|||
| Whether you have been listed on the credit blacklist by the relevant authorities |
No |
|||
| Are there any violations of the "Implementation Measures for Strengthening In-Process and Post-Event Supervision of Administrative Licensing for Laboratory Animals (Revised Edition)"? |
No |
|||
| Mid- and Post-Event Supervision Content Self-Review Status |
Changes to License Basic Information |
|||
| ( 1) Promptly update the organization’s registered information, such as the unit name, legal representative, and facility address. |
Yes, the specific change is: The company name has been changed to Shengshi Taikang Biomedical Technology (Suzhou) Co., Ltd. |
|||
| ( 2) Promptly update permit information such as facility environment, animal species, and facility area. |
No changes this year. |
|||
| ( 3) Apply for license renewal by the specified deadline. |
No continuation this year |
|||
| Implementation Status of Basic Systems |
||||
| ( 1) Develop management systems and standard operating procedures, and revise them promptly. |
Is |
|||
| ( 2) All original records related to the production of laboratory animals are complete (including personnel entry/exit, disinfection procedures, temperature and humidity levels, pressure differentials, strain preservation, breeding activities, and operation of hardware equipment). |
Is |
|||
| ( 3) Develop a biosafety emergency response plan, equip essential emergency supplies, and publicly display contact information for reporting incidents involving laboratory animals as well as emergency procedures in prominent locations. |
Is |
|||
| Management Team and Staffing Information |
||||
| ( 1) Promptly update the head of the experimental animal management and ethics committee. |
There were no changes that year. |
|||
| ( 2) Promptly update the biosafety emergency contact person and facility contact. |
There were no changes that year. |
|||
| Facility Usage and Environmental Quality Control Status |
||||
| ( 1) Promptly file a record if facilities are suspended from use or have not conducted animal experimentation activities for more than 6 months. |
Not involved |
|||
| ( 2) Regular environmental testing of the laboratory animal facilities, with complete original records for all relevant tests. |
Is |
|||
| Animal Quality, Control, and Welfare Assurance Measures |
||||
| ( 1) Regular quality inspections of animals, with complete original records of relevant tests (limited to production facilities only). |
Not involved |
|||
| ( 2) Harmlessly dispose of animal carcasses and waste materials, with complete documentation. |
Is |
|||
| ( 3) Promptly enter data into the national and provincial laboratory animal management systems. |
Is |
|||
|
|
( 4) Conduct ethical reviews of laboratory animal welfare in a standardized manner. |
Is |
||||||||||
| Other situations |
||||||||||||
| ( 1) Produce, sell, purchase, and use laboratory animals with valid quality certificates in accordance with laws and regulations. |
Is |
|||||||||||
| ( 2) Applications for science and technology awards and participation in science and technology program projects must adhere to standards for laboratory animal research and ensure complete documentation. |
Is |
|||||||||||
| ( 3) Are there any instances of outsourcing or subcontracting for animal testing? |
No |
|||||||||||
| ( 4) Do the quality of laboratory animal cage equipment meet relevant standards? Are the frames stable and secure, with smooth, even surfaces free of cracks or leaks? |
Is |
|||||||||||
| Biological Safety Management Status |
Shengshi Taikang has established a comprehensive biosafety management system and conducts regular training sessions for relevant personnel. Emergency response plans have been put in place, along with ongoing biosafety training and emergency drills. The company promptly updates the contact persons responsible for reporting biosafety emergency plans. Under the supervision and guidance of the company's safety supervisors, Shengshi Taikang actively promotes biosafety initiatives to proactively prevent potential incidents and ensure zero safety-related accidents. |
|||||||||||
| Laboratory animal personnel |
Personnel Total 4 people |
Categorized by nature (People) |
Technical personnel |
Management personnel |
Animal caretakers |
Veterinarian |
||||||
| 3 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|||||||||
| Categorized by educational level (People) |
Doctor |
Master's degree |
Bachelor |
Junior college |
||||||||
| 0 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
|||||||||
| Professionals participate in skills training and continuing education (people (per time) |
4 |
Employee Health Checkups (Persons) |
4 |
|||||||||
| Level of innovation |
Undertake Government Scientific research Project |
Conducting scientific research using laboratory animals Project |
Apply at the provincial level or above 0 Item |
Experimental Animal Research Project |
Apply at the provincial level or above 0 Item |
|||||||
| Source |
Quantity (Item) |
Funding Funding (Ten thousand yuan) |
Source |
Quantity (Item) |
Funding Funding (Ten thousand yuan) |
|||||||
| Country |
0 |
0.00 |
Country |
0 |
0.00 |
|||||||
| Provincial |
0 |
0.00 |
Provincial |
0 |
0.00 |
|||||||
| City-level |
0 |
0.00 |
City-level |
0 |
0.00 |
|||||||
| Other |
0 |
0.00 |
Other |
0 |
0.00 |
|||||||
| Total |
0 |
0 |
Total |
0 |
0 |
|||||||
| Experiment Animals Related Award-winning Situation |
Award Name |
Issuing Department |
Award Level |
|||||||||
| None |
None |
None |
||||||||||
| Experiment Animals Related Standard Develop Situation |
Application 0 Item |
Application Standard Name |
Types of standards (National Standard, Local Standard, Industry Standard, Enterprise Standard) |
Project Approval Department |
||||||||
| None |
None |
None |
||||||||||
| Project Approval 0 Item |
Project Approval Standard Name |
Types of standards (National Standard, Local Standard, Industry Standard, Enterprise Standard) |
Project Approval Department |
|||||||||
| None |
None |
None |
||||||||||
| Experiment Animals Related Paper Situation |
International 0 Article Domestic 0 Article |
Representative Paper Title (No more than 3 articles) |
Publication Venue |
First author |
||||||||
| None |
None |
None |
||||||||||
| None |
None |
None |
||||||||||
| None |
None |
None |
||||||||||
| This year, significant achievements have been made in research or industry related to laboratory animals, with a maximum of 3 items, each under 500 words |
None |
|||||||||||
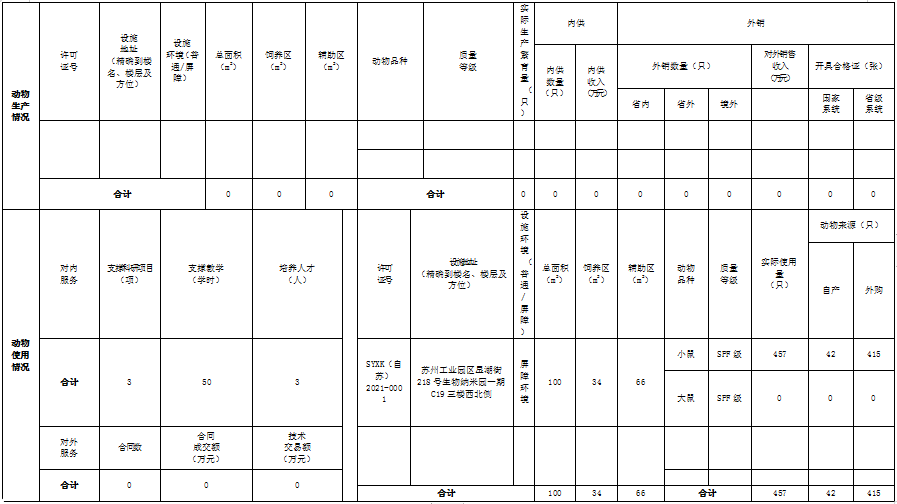
| License-issuing entity Annual Work Summary ( Within 1000 words (additional pages may be attached). |
Mainly includes: 1) The unit’s management of laboratory animals (including its management system, institutional framework, safety protocols, ethical reviews, as well as financial investment and supporting measures); 2) The annual construction and operational status of the laboratory animal facility, along with its role in supporting the development of the unit or the broader industry; 3) Any existing challenges and relevant recommendations. Shengshi Taikang Laboratory Animal Facility is located in Suzhou Free Trade Zone and falls under the jurisdiction of the Department of Biology. Its primary function is to support the breeding of research-grade laboratory animals for our company. The Department of Biology and the Quality Assurance Division regularly review and promptly update the facility’s animal-related management policies. To ensure the facility operates smoothly, routine inspections of the animal housing environment, sterilization quality checks for pressure vessels, and equipment calibration are conducted as scheduled. Additionally, the facility collaborates only with qualified suppliers to procure compliant laboratory animals, while ensuring proper disposal of animal carcasses, medical waste, and used bedding materials through safe and environmentally sound processes. For researchers, comprehensive pre-employment training is provided, and ongoing skill development programs are implemented to enhance technical expertise and standardize operational practices, thereby fostering a strong awareness of both animal welfare ethics and biosafety principles. In 2023, despite a decline in the number of research projects—and consequently, a reduction in the overall use of laboratory animals—the facility’s management remained committed to maintaining compliance with barrier facility standards and reinforcing oversight of both researchers and technical staff, ensuring uninterrupted operations. |
|
||
| License-issuing entity Opinion |
The information provided above is accurate.
Official Seal: Year Month Day |
Science and Technology Bureau of the Prefecture-Level City Annual Inspection Feedback |
Official Seal: Year Month Day |
|
Note: 1. Units holding experimental animal licenses must publicly display their annual inspection report for at least 5 working days within their organization, and submit a screenshot of the public notice along with the inspection report to the local Science and Technology Bureau.
2. Conducting research projects using laboratory animals refers to studies involving the use of experimental animals during the implementation of a scientific research project. Such projects specifically focus on activities like preserving, developing, and applying laboratory animal resources, as well as conducting research on animal quality testing techniques and quality control methods, and studying, developing, and utilizing animal models. Meanwhile, a "scientific research project" refers to initiatives organized and carried out by an institution or supported by relevant authorities.
3. The "Five Types of Technology Contracts" refer to technology development contracts, technology transfer contracts, technology licensing contracts, technology consulting contracts, and technology service contracts, all of which must be registered and certified through the "Jiangsu Province Technology Contract Recognition and Registration Platform System" (http://www.jstec.com.cn/). The contract registration number is the unique identifier assigned during the registration process on this platform. Meanwhile, the contract transaction value represents the total amount recorded for the technology contract, while the technology transaction value specifically refers to the portion of the contract transaction value that pertains to technical fees.
